We are proud to announce that SES Research’s very own powerful C60 Olive Oil product was recently used in a highly successful scientific study.
The study was done by Tarek Baati, Fanchon Bourasset, Najla Gharbi, Leila Njim, Manef Abderrabba, Abdelhamid Kerkeni, Henri Szwarc, and Fathi Moussa and published in 2012.
Researchers found that rats that consume C60 tend to have longer lifespans than those that do not consume C60.
In other words, C60 actually made these rats live longer!
The abstract reads as follows:
Countless studies showed that [60]fullerene (C60) and derivatives could have many potential biomedical applications. However, while several independent research groups showed that C60 has no acute or sub-acute toxicity in various experimental models, more than 25 years after its discovery the in vivo fate and the chronic effects of this fullerene remain unknown. If the potential of C60 and derivatives in the biomedical field have to be fulfilled these issues must be addressed. Here we show that oral administration of C60 dissolved in olive oil (0.8 mg/ml) at reiterated doses (1.7 mg/kg of body weight) to rats not only does not entail chronic toxicity but it almost doubles their lifespan. The effects of C60-olive oil solutions in an experimental model of CCl4 intoxication in rat strongly suggest that the effect on lifespan is mainly due to the attenuation of age-associated increases in oxidative stress. Pharmacokinetic studies show that dissolved C60 is absorbed by the gastro-intestinal tract and eliminated in a few tens of hours. These results of importance in the fields of medicine and toxicology should open the way for the many possible -and waited for- biomedical applications of C60 including cancer therapy, neurodegenerative disorders, and ageing.
Background on C60
Since the early 1990s, studies have shown that C60 has the potential to make waves in a variety of industries, including biology and medicine. Its antioxidant properties are hailed as extraordinary, and some even claim the substance can prevent sunburn, osteoarthritis, and help hair growth.
What is an antioxidant?
“An antioxidant is a substance that inhibits oxidation, especially one used to counteract the deterioration of stored food products, or a substance that removes potentially damaging oxidizing agents in a living organism.”
WebMD defines them as substances that “protect the body from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Many experts believe this damage is a factor in the development of blood vessel disease (atherosclerosis), cancer, and other conditions.”
They’re basically unstable molecules that can react with other molecules.
Your body is exposed to free radicals through various means, such as:
- Through by-products of normal processes that take place in your body (such as the burning of sugars for energy and the release of digestive enzymes to break down food).
- When the body breaks down certain medicines.
- Through pollutants.
How do antioxidants work?
You know that all matter in our universe is made up of atoms. And when connected together, they become molecules. The human body is made up of a bunch of these molecules, forming our DNA, proteins, fats, etc.
Humans maintain structure and function, or stay alive, through chemical reactions known as metabolism. These chemical reactions break molecules into smaller pieces, while smaller molecules are organized into larger ones.
It’s important for a molecule to be stable. In order for a molecule to be stable, it must have the correct amount of electrons. If it doesn’t, it can turn into a free radical.
Free radicals are unstable, electrically charged molecules in the cells.
When reacting with other molecules, free radicals damage other molecules, like DNA or the cell membrane. This can be very dangerous and even lead to a chain reaction, like dominoes falling. Researchers claim these free radicals may contribute to the development of health conditions like cancer.
Thankfully, antioxidants can fight back against these free radicals by giving them the electrons they need to be properly balanced, effectively neutralizing the threat.
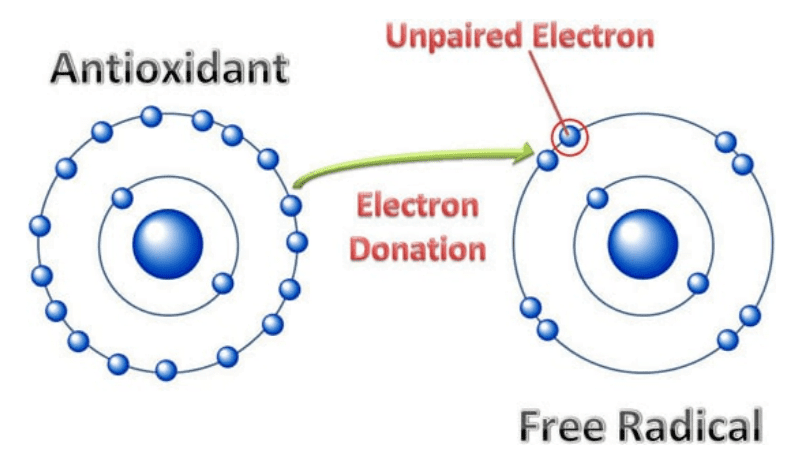 Image Source: Healthline
Image Source: Healthline
Examples of Antioxidants
Examples of antioxidants include Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin E, flavonoids (found in plants), some minerals, etc. The best place to get antioxidants is from vegetables and fruits (like acai berry), but they can also be found in some tea and red wine. They are also offered as supplements!
C60 is simply another antioxidant, which may prevent medical conditions and improve management of illness. However, the research surrounding C60 benefits has made it clear that it’s much more than a “superfood” like the acai berry – it can actually lengthen lifespans.
Researchers wanted to test the rumoured antioxidant properties of C60, which prompted this 2012 study by Baati, Bourasset, Gharbi, Njim, Abderrabba, Kerkeni, Szwarc, and Moussa.
The Study: What Happened and How They Did it
 As mentioned in the abstract, “the in vivo fate and the chronic effects of this fullerene remain unknown.” While the substance has the potential to help out various industries such as biomedicine, health, etc., its potential is yet untapped.
As mentioned in the abstract, “the in vivo fate and the chronic effects of this fullerene remain unknown.” While the substance has the potential to help out various industries such as biomedicine, health, etc., its potential is yet untapped.
The researchers set out to answer the question “What are the effects of C60 on a living organism?”
If the potential of C60 and derivatives in the biomedical field have to be fulfilled, these issues must be addressed.
The researchers obtained the C60 from SES Research in Houston, Texas.
They utilized male Wistar rats as test subjects and did a variety of tests pertaining to each subject area, as follows.
Pharmokinetics:
Rats were acclimated for seven days prior to dosing, and each had their own individual cage. These cages were housed in an air-conditioned room. The rats were given access to sufficient food and water as well as placed on a 12-hour light/dark cycle for consistency.
These rats were then catheterized, recovered for a day, and then researchers flushed the blood catheter with a 0.9% sodium chloride solution in order to “avoid possible clot obstruction.”
One night prior to treatment, the rats were fasted, but given access to water. Then, researchers injected or fed a single dose of C60 (4 mg/kg of body weight) to the rats, in 2 groups of 3 rats each.
Blood was drawn both prior to and after dosing, and urine samples were taken at 24 and 48 hours after dosing. Rats were then sacrificed for organ collection and analysis.
Biodistribution:
In this section, 4 groups of three rats were treated every day for 1 week either by injection or orally. The dose of C60 was the same as in the pharmokinetics section (4 mg/kg body weight).
Again, researchers drew blood and urine, and sacrificed the animals for organ collection.
Chronic Toxicity and Effects of C60 on Survival of Rats:
Researchers acclimated the rats for 2 weeks before proceeding with the study. Three groups of rats (6 in each group) were given C60 every day for 1 week, then weekly until the end of the second month. After that, they received C60 doses every 2 weeks until the end of the seventh month. The doses were either given by gavages (like a feeding tube) with 1 ml of water, or C60 dissolved in olive oil (0.8 mg/ml).
Chronic Toxicity: The development of adverse affects as the results of long-term exposure to a stressor substance.
Effects of C60 Olive Oil Solutions on Oxidative Stress:
Researchers divided 60 rats into 10 groups. These rats were dosed daily for 1 week (orally or injected). Group A got 1 ml of water. Groups B and C were given 1 ml of olive oil for pre-treatment. Finally, Groups D and E were pre-treated with 1 ml of C60 Olive Oil.
Oxidative Stress: An imbalance between the production of free radicals and the ability of the body to fight back, or detoxify, their harmful effects with antioxidants.
The researchers then studied the organs, urine samples, blood samples, and brain samples of the rats over time.
Conclusions of the C60 Study
Through this study, the researchers discovered the C60 has an extremely positive effect on the lifespan of rats. In fact, the discovery was pretty extraordinary:
“Our results show that while olive oil treatment can lead to an increase of 18% of lifespan of treated rats, C60-olive oil can increase it up to 90%, as compared to controls. The effects of olive-oil on health and ageing are well known, and its effect as a function of dose has been thoroughly discussed. But, what is noteworthy is that at M38 all C60-treated rats were still alive. Thus, based on previous investigations, C60 should be the most efficient ever material for extending lifespan.”
C60, as the researchers found out, is a very powerful antioxidant. It is very well armed to fight against the negative effects of free radicals. Even more interesting is the fact that during this study, the C60 dosing protected the liver.
“Pathological examinations show that even at very low doses, 500 times lower than that used previously, C60-olive oil solutions effectively protects the livers against CCl4 toxicity. These results are in agreement with those reported for very low doses of water solution of hydrated C60 fullerene in other experimental models.”
They were able to confirm, through this study, that C60 is a “powerful liver-protective agent” that operates under a “free radical scavenging mechanism.”
The researchers consider this study to “open the road towards the development of the considerable potential of C60 in the biomedical field, including cancer therapy, neurodegenerative disorders and ageing.”
Read the original study by clicking here.
Check out the Interview With Researcher Fathi Moussa
C60 Study: The prolongation of the lifespan of rats by repeated oral administration of [60] fullerene | SES Research – Houston, TX


