If you aren’t already, you should start taking antioxidants like Vitamin C, C60, and others. Below, we delve into antioxidants, how they work, and the top 5 antioxidants you should be taking to improve your health.
What are antioxidants?
“An antioxidant is a substance that inhibits oxidation, especially one used to counteract the deterioration of stored food products, or a substance that removes potentially damaging oxidizing agents in a living organism.”
WebMD defines them as substances that “protect the body from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Many experts believe this damage is a factor in the development of blood vessel disease (atherosclerosis), cancer, and other conditions.”
They’re basically unstable molecules that can react with other molecules.
Your body is exposed to free radicals through various means, such as:
- Through by-products of normal processes that take place in your body (such as the burning of sugars for energy and the release of digestive enzymes to break down food).
- When the body breaks down certain medicines.
- Through pollutants.
How do antioxidants work?
You know that all matter in our universe is made up of atoms. And when connected together, they become molecules. The human body is made up of a bunch of these molecules, forming our DNA, proteins, fats, etc.
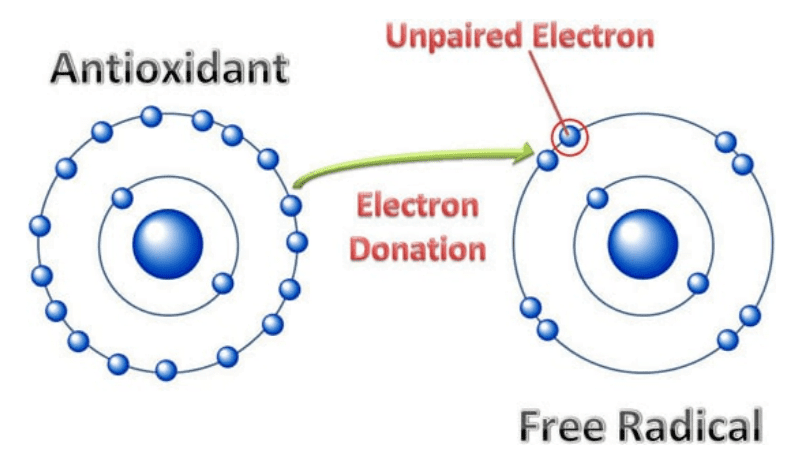
Image Source: Healthline
Humans maintain structure and function, or stay alive, through chemical reactions known as metabolism. These chemical reactions break molecules into smaller pieces, while smaller molecules are organized into larger ones.
It’s important for a molecule to be stable. In order for a molecule to be stable, it must have the correct amount of electrons. If it doesn’t, it can turn into a free radical.
Free radicals are unstable, electrically charged molecules in the cells.
When reacting with other molecules, free radicals damage other molecules, like DNA or the cell membrane. This can be very dangerous and even lead to a chain reaction, like dominoes falling. Researchers claim these free radicals may contribute to the development of health conditions like cancer.
Thankfully, antioxidants can fight back against these free radicals by giving them the electrons they need to be properly balanced, effectively neutralizing the threat.
The Top 5 Antioxidants You Should Be Taking
Check out our list of the top 5 antioxidants you should be taking to improve and maintain your health, below.
 5) Vitamin E
5) Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant compound. Though it exists in 8 chemical forms, only 1 form meets the requirements for human consumption: Alpha- (or α-) tocopherol. According to the National Institutes of Health:
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant that stops the production of ROS (reactive oxygen species) formed when fat undergoes oxidation. Scientists are investigating whether, by limiting free-radical production and possibly through other mechanisms, vitamin E might help prevent or delay the chronic diseases associated with free radicals.
The body creates ROS when converting food into energy. Antioxidants like Vitamin E may protect cells from any damage ROS causes.
How much do I need and where can I find it?
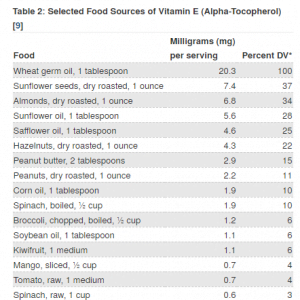
Below, you can see the NIH’s Recommended Intake for Vitamin E, as well as foods the antioxidant is commonly found in:
4) Vitamin A

Vitamin A is the name of a group of fat-soluble retinoids, including retinol, retinal, and retinyl esters. Its antioxidant properties are well known. This vitamin supports:
- immune function
- vision
- reproduction
- cell growth and communication
- heart health
- lung health
- kidney health
- maintenance of other organs
It’s especially important for vision, as it is an essential component of rhodopsin, which is a protein that absorbs light in the retinal receptors, supporting the functioning of the conjunctival membranes and cornea.
How much Vitamin A do I need?
There are two types of Vitamin A: Preformed and Provitamin A.
- Preformed — Found in meat, poultry, fish, and dairy
- Provitamin A — Found in fruits, vegetables, and plant-based products (most common type is beta-carotene)
You can find it in a variety of foods, such as:
- Beef liver and other organ meats (but these foods are also high in cholesterol, so limit the amount you eat).
- Some types of fish, such as salmon.
- Green leafy vegetables and other green, orange, and yellow vegetables, such as broccoli, carrots, and squash.
- Fruits, including cantaloupe, apricots, and mangos.
- Dairy products, which are among the major sources of vitamin A for Americans.
- Fortified breakfast cereals.
How much you need depends on your age and reproductive status. Check out the table below for recommended daily intake from the NIH:
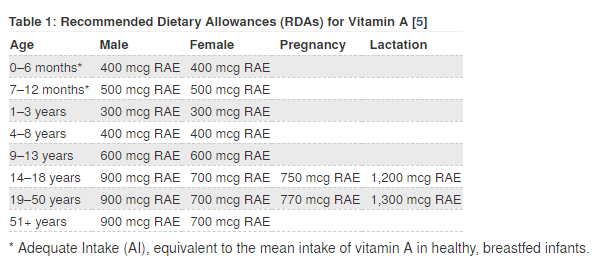
Please note that product labels don’t show Vitamin A content in mcg RAE, but rather in international units (IU). Converting between the two isn’t easy.
For adults and children 4 years and older, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration has established a vitamin A Daily Value (DV) of 5,000 IU from a varied diet of both plant and animal foods. DVs are not recommended intakes; they don’t vary by age and sex, for example. But trying to reach 100% of the DV each day, on average, is useful to help you get enough vitamin A.
 3) Resveratrol
3) Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a polyphenic bioflavonoid antioxidant made by certain plants and naturally found in food and drinks. It’s produced naturally by plants when they’re injured or being attacked by pathogens (i.e. bacteria or fungi). Its ability to fight off stressors like radiation and infections makes it a great antioxidant supplement. In fact, it’s said to be one of the most potent polyphenols and strongest protections against free radical damage and aging.
Researchers have found that resveratrol may decrease the risk of heart disease and other ailments.
The benefits of resveratrol were first discovered when researchers found that yeast, other microbes, insects, and animals that consumed resveratrol experienced an increased life span.
Various studies continued to confirm its amazing anti-aging benefits, demonstrated in studies conducted on fruit flies, fish, mice and nematode worms, all of which lived longer compared to control groups that were not treated with this phytonutrient.
It’s typically found in superfoods like red wine. Did you know that Plato even talked about the benefits of resveratrol from drinking red wine in moderation?
“Nothing more excellent or valuable than wine was ever granted by the gods to man.” – Plato
How much do I need and where can I find it?
You can typically find resveratrol in the following foods and drinks:
- red wine
- raw cocoa
- blueberries
- bilberries
- mulberries
- lingonberries
- red grapes
Dosage recommendations will vary depending on your age and current health. Usually, people take between 250 to 500 milligrams per day. It’s important to point out that this is generally lower than the amounts that have been shown to be beneficial in studies, but it’s not clear if taking very high doses is safe. They can potentially interact with blood thinners like Advil, so make sure you discuss it with your doctor first before taking this antioxidant supplement.
 2) Lycopene
2) Lycopene
Lycopene is a bright red carotene and carotenoid pigment and phytochemical found in tomatoes and other red fruits and vegetables. However, it is not found in cherries or strawberries. It’s actually registered as an official food coloring in the U.S.! Think about how spaghetti sauce stains your cookware — lycopene is usually responsible for that. It’s what gives tomatoes their bright red coloring.
Research studies suggest that taking lycopene may lower the risk of cancer or cardiovascular disease.
How much lycopene do I need?
Recommended intake has not been officially established just yet. However, according to MayoClinic, most clinical studies have focused on the amount of lycopene-containing foods that participants ate instead of the quantities consumed. Livestrong suggests:
Eating a variety of brightly colored fruits and vegetables each day may be a more effective way to prevent chronic disease than taking lycopene in supplement form, the American Cancer Society notes.
The ACS suggests eating 5 servings of deeply colored fruits and vegetables per day to get the benefits of lycopene. Benefits include:
- cancer prevention
- helps fight against HPV
- promotes eye health
- lowers neuropathic pain
- improves brain health
- lowers blood pressure
- promotes heart health
- relieves bone stress
You can find lycopene in common food and drinks such as:
- tomatoes or canned tomato paste
- watermelon
- grapefruit
- guava
- apricots
- carrots
- red cabbage
- mangoes
- papaya
Often abbreviated as C60, Carbon 60 Fullerenes already have a wide variety of uses and applications in many different fields. Research on Carbon 60 Fullerenes has uncovered compelling data regarding the potential use of C60 for a variety applications in various fields:
- b
 iomedical
iomedical - chemical research
- nanotechnology
- health and medicine
- electronics development
Click here to read about the most recent Fullerene research in medicine published in the Royal Society of Chemistry Journal.
Research suggests that C60 has antioxidant properties and can even lengthen lifespan. In a recent study with lab rats, researchers found that C60 doubled the lifespan of rats. Over the course of 30 hours, the gastrointestinal tract absorbed the dissolved buckyballs and released it from the body with no harm. Other researchers say that even though it is excreted from the body quickly, some long-lasting changes in organs and cells must have been created such as strengthening DNA. In the end, the lifespan of the rats was doubled.
“Our results show that while olive oil treatment can lead to an increase of 18% of lifespan of treated rats, C60-olive oil can increase it up to 90%, as compared to controls. The effects of olive-oil on health and ageing are well known, and its effect as a function of dose has been thoroughly discussed. But, what is noteworthy is that at M38 all C60-treated rats were still alive. Thus, based on previous investigations, C60 should be the most efficient ever material for extending lifespan.”
Carbon 60, as the researchers found out, is a very powerful antioxidant. It is very well armed to fight against the negative effects of free radicals. Even more interesting is the fact that during this study, the C60 dosing protected the liver.
“Pathological examinations show that even at very low doses, 500 times lower than that used previously, C60-olive oil solutions effectively protects the livers against CCl4 toxicity. These results are in agreement with those reported for very low doses of water solution of hydrated C60 fullerene in other experimental models.”
They were able to confirm, through this study, that C60 is a “powerful liver-protective agent” that operates under a “free radical scavenging mechanism.”
How much Carbon 60 should I take?
While proper recommended dosage has not been officially established, we have received a lot of customer feedback over the years.
The most common dosage of C60 is 1 teaspoon per day (approximately 5 ml). Our 100 ml bottle, then, would provide 20 doses. Others take a bit more, or a bit less.
You can take C60 at any time of day, with or without food. It all depends on your preferences.
Some of our athletic customers like to take their C60 before being active, which is often reported to provide a large boost in performance.
Top 5 Antioxidants You Should Be Taking | SES Research – Houston, TX



 5) Vitamin E
5) Vitamin E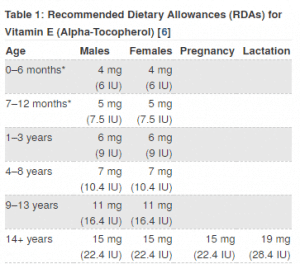
 3) Resveratrol
3) Resveratrol 2) Lycopene
2) Lycopene iomedical
iomedical